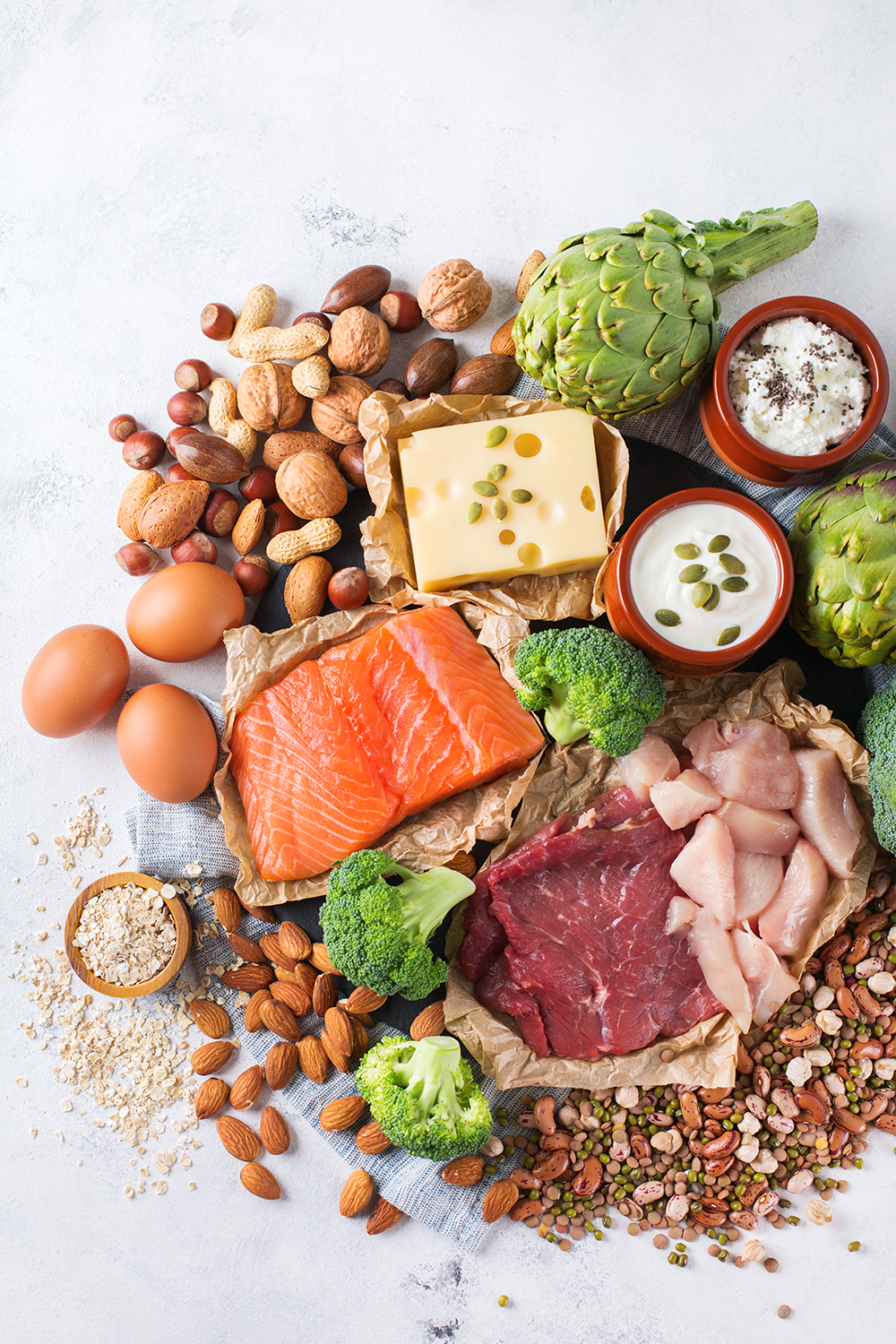
Protein is a vital building block for our body—supporting the creation of brain cells, muscles, enzymes, hormones, and more. Both plant-based and animal-derived proteins can nourish the body, providing essential micro and macronutrients that help us thrive.
How Much Protein Do You Need?
For adults, the recommended protein intake is around 0.5 grams per kilogram of body weight per day. For a typical adult weighing between 135–150 pounds, that equates to approximately 30–50 grams of protein daily. While many associate protein with meat, plant-based proteins offer a rich variety of nutrients in addition to protein.
Plant-Based Protein Sources
Variety is key when it comes to plant-based proteins, as they deliver a wide range of nutrients alongside protein:
- Vegetables (per cup):
- Broccoli (5g), Brussels Sprouts (4g), Raw Spinach (0.9g), Cooked Kale (2.5g), Boiled Peas (8.5g), Sweet Potato (5g), Cauliflower (2.2g)
- Fruit (per cup):
- Raspberries (1.4g), Strawberries (1g), Blackberries (1g), Passionfruit (5g), Grapes (1g), Banana (1.6g), Cherries (1.4g)
- Ancient Grains (per cup):
- Quinoa (8g), Barley (11g), Buckwheat (6g), Millet/Farro/Amaranth (12g), Oats (6g)
- Seeds (per ounce):
- Chia (4.7g), Pumpkin (5g), Sunflower (6g)
- Lentils & Beans (per cooked cup):
- Lentils (18g), Soybeans (17g), Black Beans (15g), Tofu (20g), Tempeh (30g)
- Nuts (per ounce):
- Almonds (6g), Cashews (4.4g), Walnuts (2.5g), Pistachios (6g), Peanuts (7g)
Animal-Based Protein Sources
If you prefer animal-derived proteins, there are plenty of nutrient-rich options to choose from:
- Dairy & Eggs:
- Milk (8g per 8oz), Plain Yogurt (10-14g per 6-8oz), Hard Cheese (7-8g per 1oz), Eggs (6g per egg)
- Meat
- Chicken Breast (31g per 4oz), Pork Loin (31g per 4oz), Steak (31g per 4oz)
- Fish
- Canned Tuna (29g per 5oz), Most Fish Fillets (22-24g per 4oz)
Don’t Forget Fiber!
In addition to protein, fiber plays a crucial role in digestive health. The goal is to consume 25–30 grams of fiber daily, with a mix of soluble and insoluble fibers to support healthy digestion.
- Soluble Fiber: Lowers cholesterol and stabilizes glucose, found in foods like oatmeal, apples, oranges, lentils, flaxseeds, and chia seeds.
- Insoluble Fiber: Promotes regular bowel movements, found in beans, wheat bran, nuts, brown rice, cauliflower, and green beans.
Probiotic-Rich Foods for a Healthy Gut
Probiotic-rich foods support your microbiome, improving gut health and digestion. Add these to your diet for a natural probiotic boost:
- Kefir, Yogurt, Kimchi, Kombucha, Non-Processed Pickles, Sauerkraut, Miso Soup, Tofu, Tempeh, Sourdough Bread, Buttermilk.
Note: Some high-probiotic foods may cause gas, so pay attention to how your body responds and choose what works best for you.
The Path to Balanced Nutrition
Achieving balanced nutrition is all about making informed, mindful food choices. Whether you’re adding more plant-based proteins, increasing your fiber intake, or incorporating probiotic-rich foods, each small step can have a significant impact on your overall health. By nourishing your body with a variety of nutrient-dense foods, you’re supporting not only your physical well-being but your mental clarity and emotional balance as well. Prioritize what fuels you best, and let your diet work for you.